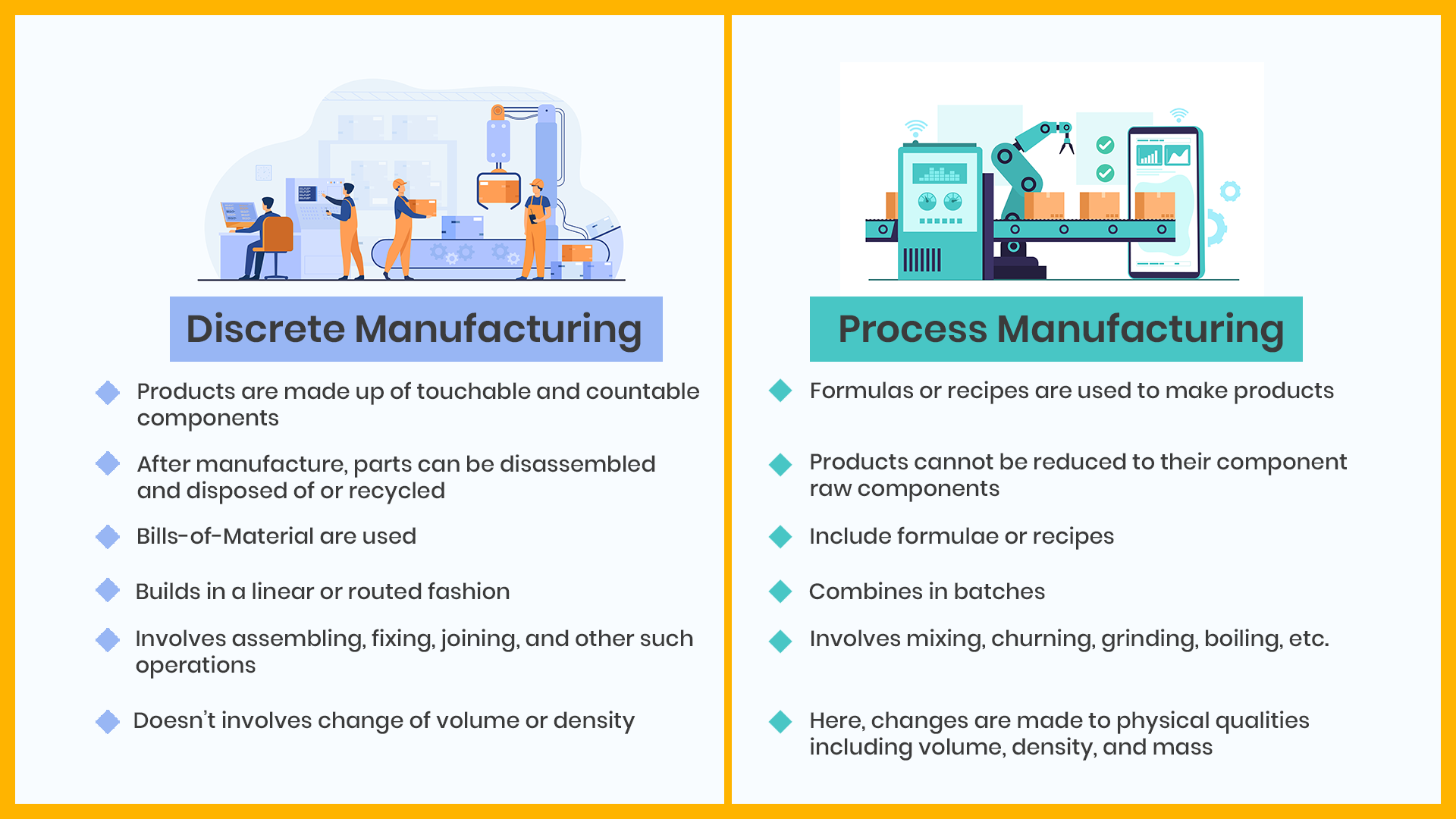
The section topic is the difference between discrete manufacturing and process manufacturing.
The main difference between the two manufacturing processes is that in process manufacturing, many of the steps are completed simultaneously. For example, in continuous casting, molten metal can be cast into several different shapes at one time. The advantage to this type of production is that it leads to more finished products and less waste than discrete production.
This means that the products come out with less defects as well, which leads to lower-costing items and a shorter overall supply chain for manufacturers.
What is discrete manufacturing?
Discrete manufacturing, also called batch production, is a method of manufacture in which each item produced is different from its predecessor. Companies relying on this type of production usually produce only one type or a small number of types of items. Discrete manufacturing is an assembly-based production process involving components, materials, and subassembles used to create discrete items such as equipment, products, and parts. From vast operations with rigid traditional production protocols to smaller operations assisted by automation, there are several approaches you can take when implementing a discrete manufacturing strategy.
Importance of discrete manufacturing
One of the main advantages of discrete manufacturing is that it helps us to make things that are more complex and diverse.
The production process of discrete parts is different from the mass production process. In mass production, there are usually large volumes of similar components. But in a discrete manufacturing process, there are different parts with a wide range of sizes or shapes.
It is often necessary to create very precise specifications for the dimensions and geometries of individual parts to ensure they will fit with other components during assembly and still have enough room for cooling or other components required in order to make them function.
The discrete manufacturing process can be broken down into three phases:
- Planning
- Production
- Delivery
Exploring Discrete Manufacturing Processes & Techniques
Define Your Discrete Manufacturing Needs.
Before determining which discrete manufacturing process to use, you need to define your project's needs. Begin by analysing the complexity of each component, the number and type of parts, and the time needed so you can accurately identify a timeline for completion. Once you understand your needs, you can identify the best manufacturing techniques to get the end product designed and manufactured.
Understand the Difference Between Standard and Adaptive Processes.
Different discrete manufacturing processes come with different levels of complexity. Standardization creates a gathering and quickly produces low-cost items but doesn’t allow for easily tailored solutions. On the other hand, adaptive processes allow for customizability, but take more time to develop and are better suited for larger projects. Knowing the difference between these processes can help you decide which process is best for your individual needs.
Optimize Production Efficiency with Automation & Robotics Techniques.
Automated and robotic technologies have revolutionized manufacturing processes, allowing for production efficiency and quality to be improved. Robotics can automate certain actions, such as moving materials or sorting products, with greater precision than can be done manually. Automating production steps reduces the costs associated with labor and mistakes caused by human error. Moreover, automation can allow for remote monitoring of product quality throughout the entire production process.
Establish a Quality Assurance & Control Plan to Monitor Performance.
Quality assurance and control are key components of discrete manufacturing operations. Establishing a QA/QC plan is essential for ensuring that products meet the required quality standards, as well as for Weighing up the increased costs associated with automating processes against the potential advantages it offers. A comprehensive QA/QC plan should include monitoring, feedback and corrective actions when needed so that processes can be adjusted if any uncharacteristic results are detected. Additionally, ongoing training of personnel in automated production techniques can help ensure that operators know and can use the correct protocols to produce consistent results.
Take Advantage of Simulation Tools to Visualize Production Performance & Improve Capabilities.
Simulation tools can be an effective way to help organizations see the potential of automation and visualize performance prior to implementing production systems across their operations. This gives companies the ability to assess not just the productivity levels that will be achievable once automated processes are in place, but also evaluates how production flows, resources asset allocation and energy consumption can be managed. By employing simulation strategies, complex problems can be solved more efficiently and quickly so that appropriate strategies for improvement can be identified and incorporated into manufacturing processes.
What is process manufacturing?
Process manufacturing, also known as mass production, involves the creation of many identical products from components that are put together as they are needed. It's suitable for large-scale production and offers lower per-unit costs than batch production methods because both parts and labour costs are spread over many units." Process manufacturing is a production system used in many industries to streamline operations, optimize resources, and maximize profits. With this comprehensive guide, you'll learn how to fulfill customer demands more efficiently and make your process manufacturing systems more reliable.

Importance of process manufacturing
Process manufacturing is the most important part of any business. Processes are what make a company successful and profitable. They are also what will define the future of a company and help them to innovate and adapt with the changing industry landscape.
It is important for a company to put in enough effort into its processes because this will make a huge difference. It's also worth noting that process manufacturing has been rapidly changing over the past few years, so it's important to stay on top of these changes in order to survive in this competitive market.
A process is a sequence of operations or treatments applied to raw materials or semi-finished goods to produce the finished product. Manufacturing process is a series of manufacturing operations that transform various types of raw material into finished goods.
The manufacturing process can be subdivided into the following steps:
- Planning
- Designing
- Production
- Production Control v Production Maintenance
- Product Finalization
- Product Distribution
The Most Effective Strategies for Process Manufacturing
Invest in Automation.
Automation is one of the most effective strategies for process manufacturing. Automating production can reduce costs, increase throughput, and improve accuracy. It can also reduce the need for manual labor and make it easier to integrate material handling, packaging, and other quality control processes into your production system. Investing in automation is an excellent way to save time and money while boosting your profits.
Use Real-Time Data to Enhance Efficiency.
Real-time data plays an increasingly important role in process manufacturing. By harnessing the power of real-time data, manufacturers can make more informed decisions and enhance operational efficiency. Real-time data can be used to monitor workflows, identify bottlenecks, and anticipate problems before they occur. It can also be used to adjust equipment for maximum production output, streamline resource allocation, and optimize material utilization. By using real-time data effectively, process manufacturers can stay ahead of the competition and maximize their profits.
Implement Lean Manufacturing Strategies.
Implementing lean manufacturing strategies can help process manufacturers improve their production processes and become more efficient. Lean manufacturing is a process improvement strategy that uses principles such as waste reduction, process optimization, and value stream mapping to maximize production output at the lowest possible cost. By eliminating non-value adding activities and streamlining resource allocation, process manufacturers can decrease costs and increase profits.
Streamline Scheduling and Planning Processes.
Effective scheduling and planning of resources is essential to optimizing production processes in process manufacturing. Allocate the required resources for upcoming production jobs so that manufacturing runs smoothly and efficiently. Utilize advanced process scheduling software as it can provide a platform for coordinating tasks, help predict production bottlenecks, and enable users to anticipate future needs. Also consider deploying simulation tools which enable companies to test proposed scenarios and optimize their operations without taking the risk of changing physical assets.
Prioritize Quality Control and Product Testing.
Quality control and product testing play a vital role in ensuring that finished products are safe, compliant, and meet customer specifications. To ensure consistent quality of products, implement processes for testing raw materials, validating production processes and testing end products. Utilize production data analytics to track performance metrics such as defect rate and optimize process parameters accordingly to guarantee high-quality final product. Additionally, ensure compliance with industry norms and company standards through documentation and training of personnel.